Ordinamento del secchio è una tecnica di ordinamento che prevede la divisione degli elementi in vari gruppi, o secchi. Questi secchi sono formati distribuendo uniformemente gli elementi. Una volta divisi in contenitori, gli elementi possono essere ordinati utilizzando qualsiasi altro algoritmo di ordinamento. Infine, gli elementi ordinati vengono raccolti insieme in modo ordinato.
Algoritmo di ordinamento del bucket:
Creare N contenitori vuoti (o elenchi) ed eseguire le operazioni seguenti per ogni elemento dell'array arr[i].
- Inserisci arr[i] nel bucket[n*array[i]]
- Ordina i singoli bucket utilizzando l'ordinamento per inserzione.
- Concatena tutti i bucket ordinati.
Come funziona l'ordinamento dei bucket?
Per applicare l'ordinamento per bucket sull'array di input [0,78, 0,17, 0,39, 0,26, 0,72, 0,94, 0,21, 0,12, 0,23, 0,68] , seguiamo questi passaggi:
Passo 1: Crea un array di dimensione 10, dove ogni slot rappresenta un bucket.
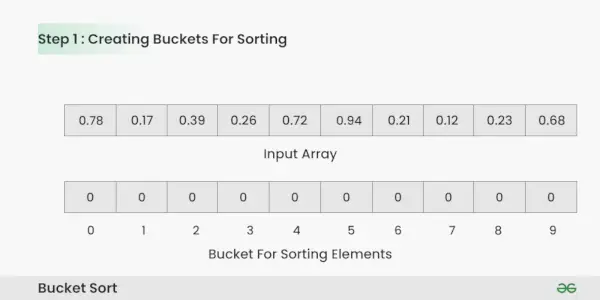
Creazione di bucket per l'ordinamento
Passo 2: Inserisci gli elementi nei bucket dall'array di input in base al loro intervallo.
Inserimento degli elementi nei bucket:
- Prendi ogni elemento dall'array di input.
- Moltiplica l'elemento per la dimensione dell'array del bucket (10 in questo caso). Ad esempio, per l'elemento 0,23, otteniamo 0,23 * 10 = 2,3.
- Converti il risultato in un numero intero, che ci fornisce l'indice del bucket. In questo caso, 2.3 viene convertito nell'intero 2.
- Inserisci l'elemento nel bucket corrispondente all'indice calcolato.
- Ripeti questi passaggi per tutti gli elementi nell'array di input.
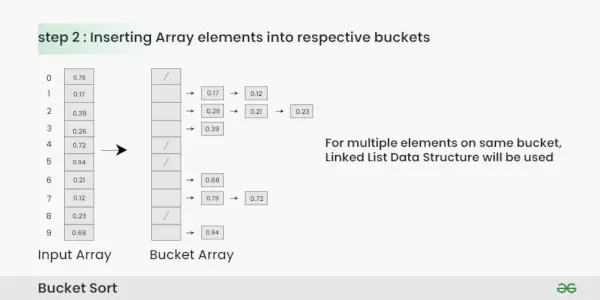
Inserimento di elementi Array nei rispettivi bucket
Passaggio 3: Ordina gli elementi all'interno di ciascun secchio. In questo esempio, utilizziamo Quicksort (o qualsiasi algoritmo di ordinamento stabile) per ordinare gli elementi all'interno di ciascun bucket.
Ordinamento degli elementi all'interno di ciascun bucket:
- Applicare un algoritmo di ordinamento stabile (ad esempio Bubble Sort, Merge Sort) per ordinare gli elementi all'interno di ciascun bucket.
- Gli elementi all'interno di ciascun bucket sono ora ordinati.
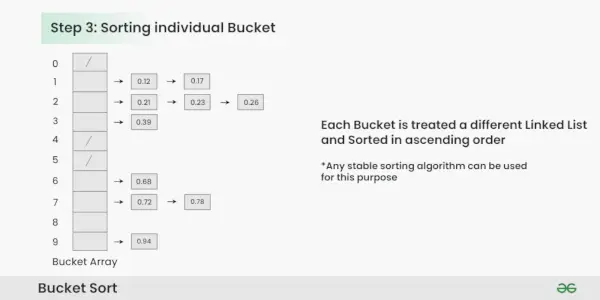
Ordinamento del singolo secchio
ordinamento Java arraylist
Passaggio 4: Raccogli gli elementi da ciascun secchio e rimettili nell'array originale.
Raccolta degli elementi da ciascun secchio:
- Scorri ogni bucket in ordine.
- Inserisci ogni singolo elemento dal bucket nell'array originale.
- Una volta copiato, un elemento viene rimosso dal bucket.
- Ripeti questo processo per tutti i secchi finché tutti gli elementi non sono stati raccolti.
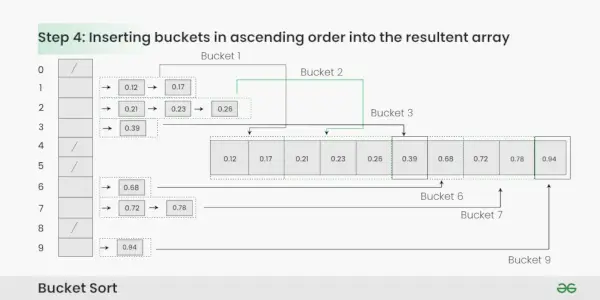
Inserimento di bucket in ordine crescente nell'array risultante
Passaggio 5: L'array originale ora contiene gli elementi ordinati.
L'array ordinato finale utilizzando l'ordinamento per bucket per l'input specificato è [0,12, 0,17, 0,21, 0,23, 0,26, 0,39, 0,68, 0,72, 0,78, 0,94].

Restituisce l'array ordinato
Implementazione dell'algoritmo di ordinamento del bucket:
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione per Bucket Sort:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; // Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets void insertionSort(vector& secchio) { for (int i = 1; i< bucket.size(); ++i) { float key = bucket[i]; int j = i - 1; while (j>= 0 && secchio[j]> chiave) { secchiello[j + 1] = secchiello[j]; J--; } secchio[j + 1] = chiave; } } // Funzione per ordinare arr[] di dimensione n utilizzando bucket sort void bucketSort(float arr[], int n) { // 1) Crea n vettore di bucket vuotib[n]; // 2) Metti gli elementi dell'array in contenitori diversi per (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { int bi = n * arr[i]; b[bi].push_back(arr[i]); } // 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { insertionSort(b[i]); } // 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[] int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < b[i].size(); j++) { arr[index++] = b[i][j]; } } } // Driver program to test above function int main() { float arr[] = {0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434}; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); bucketSort(arr, n); cout << 'Sorted array is
'; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << arr[i] << ' '; } return 0; }>
Giava import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Main { // Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets public static void insertionSort(Listsecchio) { for (int i = 1; i< bucket.size(); ++i) { float key = bucket.get(i); int j = i - 1; while (j>= 0 && bucket.get(j)> chiave) { bucket.set(j + 1, bucket.get(j)); J--; } bucket.set(j + 1, chiave); } } // Funzione per ordinare arr[] di dimensione n utilizzando bucket sort public static void bucketSort(float[] arr) { int n = arr.length; // 1) Crea n elenco di bucket vuoti[] bucket = nuovo ArrayList[n]; for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { buckets[i] = new ArrayList(); } // 2) Put array elements in different buckets for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int bi = (int) (n * arr[i]); buckets[bi].add(arr[i]); } // 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { insertionSort(buckets[i]); } // 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[] int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].size(); j++) { arr[index++] = buckets[i].get(j); } } } // Driver program to test above function public static void main(String[] args) { float[] arr = {0.897f, 0.565f, 0.656f, 0.1234f, 0.665f, 0.3434f}; bucketSort(arr); System.out.println('Sorted array is:'); for (float num : arr) { System.out.print(num + ' '); } } }> Pitone def insertion_sort(bucket): for i in range(1, len(bucket)): key = bucket[i] j = i - 1 while j>= 0 e bucket[j]> chiave: bucket[j + 1] = bucket[j] j -= 1 bucket[j + 1] = chiave def bucket_sort(arr): n = len(arr) bucket = [[] for _ in range(n)] # Inserisci gli elementi dell'array in contenitori diversi for num in arr: bi = int(n * num) buckets[bi].append(num) # Ordina i singoli contenitori utilizzando l'ordinamento di inserimento for bucket in buckets: insert_sort (bucket) # Concatena tutti i bucket in arr[] indice = 0 for bucket in buckets: for num in bucket: arr[index] = num indice += 1 arr = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434] bucket_sort (arr) print('L'array ordinato è:') print(' '.join(map(str, arr)))> C# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Program { // Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets static void InsertionSort(Listsecchio) { for (int i = 1; i< bucket.Count; ++i) { float key = bucket[i]; int j = i - 1; while (j>= 0 && secchio[j]> chiave) { secchiello[j + 1] = secchiello[j]; J--; } secchio[j + 1] = chiave; } } // Funzione per ordinare arr[] di dimensione n utilizzando bucket sort static void BucketSort(float[] arr) { int n = arr.Length; // 1) Crea n elenco di bucket vuoti[] bucket = nuova lista[N]; for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { buckets[i] = new List(); } // 2) Metti gli elementi dell'array in contenitori diversi per (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { int bi = (int)(n * arr[i]); buckets[bi].Add(arr[i]); } // 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { InsertionSort(buckets[i]); } // 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[] int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].Count; j++) { arr[index++] = buckets[i][j]; } } } // Driver program to test above function static void Main(string[] args) { float[] arr = { 0.897f, 0.565f, 0.656f, 0.1234f, 0.665f, 0.3434f }; BucketSort(arr); Console.WriteLine('Sorted array is:'); foreach (float num in arr) { Console.Write(num + ' '); } } }> JavaScript function insertionSort(bucket) { for (let i = 1; i < bucket.length; ++i) { let key = bucket[i]; let j = i - 1; while (j>= 0 && secchio[j]> chiave) { secchiello[j + 1] = secchiello[j]; J--; } secchio[j + 1] = chiave; } } function bucketSort(arr) { let n = arr.length; let bucket = Array.from({lunghezza: n}, () => []); // Inserisci gli elementi dell'array in contenitori diversi per (let i = 0; i< n; i++) { let bi = Math.floor(n * arr[i]); buckets[bi].push(arr[i]); } // Sort individual buckets using insertion sort for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { insertionSort(buckets[i]); } // Concatenate all buckets into arr[] let index = 0; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < buckets[i].length; j++) { arr[index++] = buckets[i][j]; } } } let arr = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434]; bucketSort(arr); console.log('Sorted array is:'); console.log(arr.join(' '));> Produzione
Sorted array is 0.1234 0.3434 0.565 0.656 0.665 0.897>
Analisi della complessità dell'algoritmo di ordinamento del bucket:
Complessità temporale: SU2),
- Se assumiamo che l'inserimento in un bucket richieda un tempo O(1), allora i passaggi 1 e 2 dell'algoritmo precedente richiedono chiaramente un tempo O(n).
- L'O(1) è facilmente possibile se utilizziamo una lista concatenata per rappresentare un bucket.
- Anche il passaggio 4 richiede tempo O(n) poiché ci saranno n elementi in tutti i contenitori.
- Il passaggio principale da analizzare è il passaggio 3. Anche questo passaggio richiede in media un tempo O(n) se tutti i numeri sono distribuiti uniformemente.
Spazio ausiliario: O(n+k)
