Parliamo di come creare un DataFrame vuoto e aggiungervi righe e colonne in Panda e Pitone . Esistono diversi modi in cui possiamo svolgere questo compito. Qui tratteremo la seguente sezione:
- Creazione di un Dataframe vuoto in Panda
- Aggiungi riga a Dataframe in Pandas
- Aggiungi riga a Dataframe in Pandas
Creazione di Dataframe vuoto
Creazione di un oggetto DataFrame vuoto.
Python3
# import pandas library as pd> import> pandas as pd> df>=> pd.DataFrame()> print>(df)> |
>
>
Produzione:
Empty DataFrame Columns: [] Index: []>
Aggiungi colonna a Dataframe a DataFrame vuoto
Esempio 1: Crea un DataFrame vuoto completo senza nome di colonna o indici e poi aggiungi colonne in Pandas uno per uno ad esso.
Python3
esempi di codice Java
# import pandas library as pd> import> pandas as pd> # create an Empty DataFrame object> df>=> pd.DataFrame()> print>(df)> # append columns to an empty DataFrame> df[>'Name'>]>=> [>'Ankit'>,>'Ankita'>,>'Yashvardhan'>]> df[>'Articles'>]>=> [>97>,>600>,>200>]> df[>'Improved'>]>=> [>2200>,>75>,>100>]> df> |
>
>
Produzione:
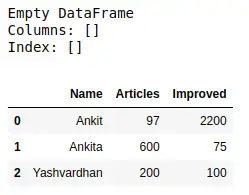
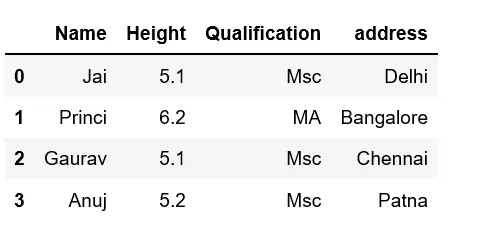
Esempio 2: Questo metodo creerà un nuovo Dataframe con una nuova colonna aggiunta al vecchio Dataframe utilizzando assegnare in Panda.
Python3
# Import pandas package> import> pandas as pd> # Define a dictionary containing Students data> data>=> {>'Name'>: [>'Jai'>,>'Princi'>,>'Gaurav'>,>'Anuj'>],> >'Height'>: [>5.1>,>6.2>,>5.1>,>5.2>],> >'Qualification'>: [>'Msc'>,>'MA'>,>'Msc'>,>'Msc'>]}> # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame> df>=> pd.DataFrame(data)> # Using 'Address' as the column name and equating it to the list> df2>=> df.assign(address>=>[>'Delhi'>,>'Bangalore'>,>'Chennai'>,>'Patna'>])> # Observe the result> print>(df2)> |
>
>
Produzione:
Aggiungi riga a DataFrame vuoto
Esempio 1: Crea un DataFrame vuoto solo con il nome delle colonne, quindi aggiungi le righe una per una utilizzando aggiungere() metodo .
Python3
nodo elenco Java
# import pandas library as pd> import> pandas as pd> # create an Empty DataFrame> # object With column names only> df>=> pd.DataFrame(columns>=> [>'Name'>,>'Articles'>,>'Improved'>])> print>(df)> # append rows to an empty DataFrame> df>=> df.append({>'Name'> :>'Ankit'>,>'Articles'> :>97>,>'Improved'> :>2200>},> >ignore_index>=> True>)> df>=> df.append({>'Name'> :>'Aishwary'>,>'Articles'> :>30>,>'Improved'> :>50>},> >ignore_index>=> True>)> df>=> df.append({>'Name'> :>'yash'>,>'Articles'> :>17>,>'Improved'> :>220>},> >ignore_index>=> True>)> df> |
>
>
Produzione:
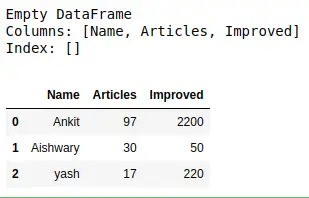
Esempio 2: Crea un DataFrame vuoto con un nome di colonna e indici e poi aggiungere righe uno per uno utilizzando il file posto[] metodo.
Python3
len dell'array in Java
# import pandas library as pd> import> pandas as pd> # create an Empty DataFrame object With> # column names and indices> df>=> pd.DataFrame(columns>=> [>'Name'>,>'Articles'>,>'Improved'>],> >index>=> [>'a'>,>'b'>,>'c'>])> print>(>'Empty DataFrame With NaN values :
'>, df)> # adding rows to an empty> # dataframe at existing index> df.loc[>'a'>]>=> [>'Ankita'>,>50>,>100>]> df.loc[>'b'>]>=> [>'Ankit'>,>60>,>120>]> df.loc[>'c'>]>=> [>'Harsh'>,>30>,>60>]> df> |
>
>
Produzione:

