Albero binario è una struttura di dati non lineare di tipo albero utilizzata principalmente per l'ordinamento e la ricerca poiché memorizza i dati in forma gerarchica. In questa sezione impareremo il implementazione della struttura dati ad albero binario in Java . Inoltre, fornisce una breve descrizione della struttura dei dati dell'albero binario.
Albero binario
Un albero in cui ciascun nodo (genitore) ha al massimo due nodi figli (sinistro e destro) è chiamato albero binario. Il nodo più in alto è chiamato nodo radice. In un albero binario un nodo contiene i dati e il puntatore (indirizzo) del nodo figlio sinistro e destro.
IL altezza di un albero binario è il numero di bordi tra la radice dell'albero e la sua foglia più lontana (più profonda). Se l'albero lo è vuoto , l'altezza è 0 . L'altezza del nodo è indicata da H .
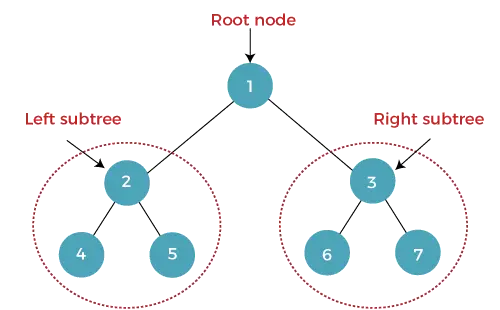
L'altezza dell'albero binario sopra è 2.
Possiamo calcolare il numero di foglie e nodo utilizzando la seguente formula.
- Il numero massimo di nodi foglia è un albero binario: 2H
- Il numero massimo di nodi è un albero binario: 2h+1-1
Dove h è l'altezza dell'albero binario.
Esempio di albero binario

Tipi di albero binario
Esistono i seguenti tipi di albero binario nella struttura dei dati:
- Albero completo/strettamente binario
- Albero binario completo
- Albero binario perfetto
- Bilanciamento dell'albero binario
- Albero binario radicato
- Albero binario degenerato/patologico
- Albero binario esteso
- Albero binario distorto
- Albero binario inclinato a sinistra
- Albero binario inclinato a destra
- Albero binario filettato
- Albero binario a thread singolo
- Albero binario a doppia filettatura
Implementazione dell'albero binario in Java
Esistono molti modi per implementare l'albero binario. In questa sezione implementeremo l'albero binario utilizzando la struttura dati LinkedList. Insieme ad esso, implementeremo anche gli ordini di attraversamento, ricercando un nodo e inserendo un nodo in un albero binario.
Implementazione dell'albero binario utilizzando LinkedList
Algoritmo
Definire la classe Node che contiene tre attributi, vale a dire: dati sinistra e destra. Qui, left rappresenta il figlio sinistro del nodo e right rappresenta il figlio destro del nodo.
- Quando viene creato un nodo, i dati passeranno all'attributo dati del nodo e sia la sinistra che la destra verranno impostate su null.
- Definire un'altra classe che ha una radice di attributo.
- Root rappresenta il nodo radice dell'albero e lo inizializza su null.
- Controlla se la radice è nulla, il che significa che l'albero è vuoto. Aggiungerà il nuovo nodo come root.
- Altrimenti, aggiungerà root alla coda.
- La variabile node rappresenta il nodo corrente.
- Innanzitutto, controlla se un nodo ha un figlio sinistro e uno destro. Se sì, aggiungerà entrambi i nodi alla coda.
- Se il figlio sinistro non è presente, aggiungerà il nuovo nodo come figlio sinistro.
- Se è presente il nodo sinistro, verrà aggiunto il nuovo nodo come figlio destro.
- Attraversa l'intero albero, quindi stampa il figlio sinistro seguito dalla radice, quindi seguito dal figlio destro.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Produzione:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Operazioni sugli alberi binari
Su un albero binario è possibile eseguire le seguenti operazioni:
conversione da stringa a intera in Java
- Inserimento
- Cancellazione
- Ricerca
- Traversata
Programma Java per inserire un nodo nell'albero binario
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Produzione:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Programma Java per eliminare un nodo in Java
Algoritmo
- Partendo dalla radice, trova il nodo più profondo e più a destra nell'albero binario e nel nodo che vogliamo eliminare.
- Sostituisci i dati del nodo più a destra con il nodo da eliminare.
- Quindi elimina il nodo più profondo a destra.
Considera la figura seguente.

EliminaNodo.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Produzione:
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Programma Java per cercare un nodo nell'albero binario
Algoritmo
- Definire la classe Node che ha tre attributi, vale a dire: dati sinistra e destra. Qui, left rappresenta il figlio sinistro del nodo e right rappresenta il figlio destro del nodo.
- Quando viene creato un nodo, i dati passeranno all'attributo dati del nodo e sia la sinistra che la destra verranno impostate su null.
- Definire un'altra classe che ha due attributi root e flag.
- Root rappresenta il nodo radice dell'albero e lo inizializza su null.
- Il Flag verrà utilizzato per verificare se il nodo indicato è presente o meno nell'albero. Inizialmente, sarà impostato su false.
- Controlla se la radice è nulla, il che significa che l'albero è vuoto.
- Se l'albero non è vuoto, confronterà i dati temporanei con valore. Se sono uguali, imposterà il flag su true e restituirà.
- Attraversa il sottoalbero sinistro chiamando ricorsivamente searchNode() e controlla se il valore è presente nel sottoalbero sinistro.
- Attraversa il sottoalbero destro chiamando ricorsivamente searchNode() e controlla se il valore è presente nel sottoalbero destro.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Produzione:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Attraversamento dell'albero binario
| Ordine trasversale | Prima visita | Seconda visita | Terza visita |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al fine | Visita il sottoalbero di sinistra in ordine | Visita il nodo radice | Visita il sottoalbero destro in ordine |
| Ordine prestabilito | Visita il nodo radice | Visita il sottoalbero sinistro in preordine | Visita il sottoalbero destro in preordine |
| Per corrispondenza | Visita il sottoalbero sinistro in postordine | Visita il sottoalbero destro in postordine | Visita il nodo radice |
Nota: ad eccezione dei tre attraversamenti precedenti, esiste un altro ordine di attraversamento chiamato attraversamento del confine.
Programma Java per attraversare l'attraversamento in ordine, preordine e postordine
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Produzione:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
Oltre alle operazioni di cui sopra, possiamo anche eseguire operazioni come nodo grande, nodo più piccolo e somma di tutti i nodi.
Programma Java per trovare il nodo più grande nell'albero binario
LargestNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Produzione:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Programma Java per trovare il nodo più piccolo nell'albero binario
Algoritmo
- Definire la classe Node che ha tre attributi vale a dire: dati, sinistra e destra. Qui, left rappresenta il figlio sinistro del nodo e right rappresenta il figlio destro del nodo.
- Quando viene creato un nodo, i dati passeranno all'attributo dati del nodo e sia la sinistra che la destra verranno impostate su null.
- Definire un'altra classe che ha una radice di attributo.
Radice rappresenta il nodo radice dell'albero e inizializzalo su null.
- Controlla se la radice è nulla , il che significa che l'albero è vuoto.
- Se l'albero non è vuoto, definisci una variabile min che memorizzerà i dati temporanei.
- Scopri il nodo minimo nel sottoalbero sinistro chiamando ricorsivamente SmallElement(). Memorizza quel valore in leftMin. Confronta il valore di min con leftMin e memorizza il minimo di due in min.
- Scopri il nodo minimo nel sottoalbero destro chiamando ricorsivamente SmallElement(). Memorizza quel valore in rightMin. Confronta il valore di min con rightMin e memorizza il massimo di due in min.
- Alla fine, min conterrà il nodo più piccolo dell'albero binario.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Produzione:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Programma Java per trovare la larghezza massima di un albero binario
Algoritmo
- Definire la classe Node che ha tre attributi, vale a dire: dati sinistra e destra. Qui, left rappresenta il figlio sinistro del nodo e right rappresenta il figlio destro del nodo.
- Quando viene creato un nodo, i dati passeranno all'attributo dati del nodo e sia la sinistra che la destra verranno impostate su null.
- Definire un'altra classe che ha una radice di attributo.
Radice rappresenta il nodo radice dell'albero e lo inizializza su null.
- La variabile maxWidth memorizzerà il numero massimo di nodi presenti in qualsiasi livello.
- La coda viene utilizzata per attraversare l'albero binario a livello di livello.
- Controlla se la radice è nulla, il che significa che l'albero è vuoto.
- In caso contrario, aggiungi il nodo root alla coda. La variabile nodesInLevel tiene traccia del numero di nodi in ciascun livello.
- Se nodesInLevel > 0, rimuove il nodo dalla parte anteriore della coda e aggiunge il figlio sinistro e destro alla coda. Per la prima iterazione, il nodo 1 verrà rimosso e i suoi nodi figli 2 e 3 verranno aggiunti alla coda. Nella seconda iterazione, il nodo 2 verrà rimosso, i suoi figli 4 e 5 verranno aggiunti alla coda e così via.
- MaxWidth memorizzerà max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel). Quindi, in qualsiasi momento, rappresenterà il numero massimo di nodi.
- Ciò continuerà finché non saranno attraversati tutti i livelli dell'albero.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Produzione:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
