Dato un numero n, trovare tutte le sequenze binarie di lunghezza 2n tali che la somma dei primi n bit sia uguale alla somma degli ultimi n bit.
Esempi:
perché la stringa è immutabile in Java
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
L'idea è di correggere il primo e l'ultimo bit e poi ripetere per i rimanenti 2*(n-1) bit. Ci sono quattro possibilità quando correggiamo il primo e l'ultimo bit:
- Il primo e l'ultimo bit sono 1 rimanenti n - Anche i bit 1 su entrambi i lati dovrebbero avere la stessa somma.
- Il primo e l'ultimo bit sono 0 rimanenti. Anche n - 1 bit su entrambi i lati dovrebbero avere la stessa somma.
- Il primo bit è 1 e l'ultimo bit è 0 la somma dei restanti n - 1 bit sul lato sinistro dovrebbe essere 1 inferiore alla somma degli n -1 bit sul lato destro.
- Il primo bit è 0 e l'ultimo bit è 1 la somma degli n-1 bit rimanenti sul lato sinistro dovrebbe essere 1 in più rispetto alla somma degli n-1 bit sul lato destro.
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione dell'idea di cui sopra:
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include
// Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char out[] int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { System.out.print(out); System.out.print(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void main (String[] args) { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array out[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences(diff out start end): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2): return; # if all bits are filled if (start > end): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if (diff == 0): print(''.join(list(out))end=' '); return; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # Driver program # input number n = 2; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out=['']*(2*n); findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); # This code is contributed by mits
// C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char []outt int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { Console.Write(outt); Console.Write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences($diff $out $start $end) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2)) return; // if all bits are filled if ($start > $end) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ($diff == 0) print(implode(''$out).' '); return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out[$start] = '0'; $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out[$start] = '1'; $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out=array_fill(02*$n''); findAllSequences(0 $out 0 2*$n - 1); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?> <script> // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences(diff outt start end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2 10)) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { document.write(outt.join('')); document.write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // input number let n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1); // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); </script>
Produzione
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Complessità temporale: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N a causa di 4 chiamate ricorsive e N (semplificato da 2N) per il tempo impiegato a stampare stringhe di dimensione 2N
Spazio ausiliario: SU)
Esiste un altro approccio mediante il quale generiamo tutte le possibili stringhe di lunghezza n e le memorizziamo in una lista in un indice che rappresenta la loro somma. Quindi iteriamo su ogni elenco e generiamo le stringhe di dimensione 2n stampando ciascuna stringa con tutte le altre stringhe nell'elenco che si sommano allo stesso valore.
C++// C++ program to implement the approach #include
// Java program to implement the approach import java.util.*; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences(int n) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.add( new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum( n sumToString new ArrayList<String>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum( int n ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString ArrayList<String> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if (n == 0) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = ''; for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) { seq = seq + sequence.get(i); } ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar); x.add(seq); sumToString.set(sumSoFar x); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.remove(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1); sequence.remove(0); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences( ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for (int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) { // Append for (int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence1++) { for (int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence2++) { if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1) { System.out.print('1111'); } else { System.out.println( sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence1) + sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence2)); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call findAllSequences(2); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
def findAllSequences(n): sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0) permuteSequences(sumToString) def generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0: sumToString[sumSoFar].append(''.join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence.append('0') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar) sequence.pop() #Generate sequence +1 sequence.append('1') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1) sequence.pop() def permuteSequences(sumToString): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString: # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr: for sequence2 in sumIndexArr: print(sequence1 + sequence2) findAllSequences(2) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { static void findAllSequences(int n) { List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>(); for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString new List<string>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n List<List<string>> sumToString List<string> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = ''; for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++) { seq = seq + sequence[i]; } sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.Add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.RemoveAt(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.Add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.RemoveAt(0); } static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++) { for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1) { Console.Write('1111'); } else { Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]); } } } } } static void Main() { findAllSequences(2); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
<script> function findAllSequences(n) { let sumToString = []; for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } function generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join('')); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.push('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.shift(); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.push('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.shift(); } function permuteSequences(sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++) { for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1) { document.write('1111'); } else { document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + ''); } } } } } findAllSequences(2); // This code is contributed by decode2207. </script>
Produzione
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Analisi della complessità temporale:
generareSequenzeConSomma = O((2N)*N)
- 2N: generiamo tutte le permutazioni di stringhe binarie di dimensione N
- N: converte l'elenco di caratteri in una stringa e memorizza nell'array. Questo viene fatto nel caso base.
permuteSequences = O((2N) * N!/(N/2)!2* N)
- 2N: iteriamo attraverso tutta la stringa generata di dimensione n
- N!/(N/2)!2: Questo è un po' difficile da spiegare
prendiamo come esempio N = 2. Il nostro array di possibili sequenze di dimensione n sarebbe:
int a char
| indice dell'array | 1 | 2 | |
| elenco di stringhe | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
Nell'elenco di stringhe di cui l'indice rappresenta la somma otteniamo il conteggio delle stringhe di dimensione 2n utilizzando la formula 'n scegli k'. Nel nostro caso sarebbe nCk *nCk dove k rappresenta il numero di 1 in ciascuna metà della stringa di dimensione 2n:
k = 0 abbiamo (2C0)^2 = 1 stringa (0000)
k = 1 abbiamo (2C1)^2 stringa = 4 stringhe(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 abbiamo (2c2)^2 = 1 stringa (1111)
Otteniamo la nostra lista di stringhe più lunga quando k = N/2 quindiNCN/2= N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] che semplifica inNCN/2= N!/(N/2)!2
Quindi per ogni elemento dobbiamo ripetere al massimoNCN/2per formare stringhe di lunghezza 2N
Senza dimostrazione formale se rappresentiamo graficamente 2^N e N!/(N/2)!2vediamo che 2Nha un tasso di crescita più veloce di quest’ultimo. Pertanto O(2N*N!/(N/2)2)< O(2N*2N) = O(22n) = O(4N)
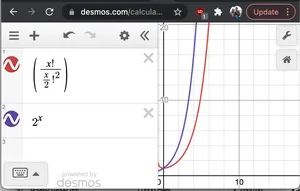 Grafico di 2^x e nC(n/2)
Grafico di 2^x e nC(n/2)- N: dobbiamo stampare ogni stringa di dimensione 2N
Infine possiamo ignorare la complessità temporale di generateSequencesWithSum perché permuteSequence è il termine principale
Complessità temporale: O(2N*N!/(N/2)!2* N) (migliore della prima soluzione di O((4^N) * N vedere la spiegazione sopra per ulteriori dettagli)
Spazio ausiliario : O(2N) perché memorizziamo tutte le permutazioni di stringhe binarie di dimensione N
formato stringa in Java
#include
import java.util.*; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data; int sum; FirstHalf(String data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map<Integer ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); //first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new ArrayList<>(); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString(String s) { int sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(char c: s.toCharArray()) { sum += c - '0'; } return sum; } public static void perm(String p char[] bin int level int n) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if(level == 0) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map.putIfAbsent(sum new ArrayList<String>()); map.get(sum).add(p); return; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(char c: bin) { perm(p+c bin level-1 n); } } public static void result() { int i = 0; for(FirstHalf first: firstHalf) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList<String> secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(String second: secondHalf) { //append first and second half and print System.out.print(first.data+second+' '); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) System.out.println(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { char[] up = {'0' '1'}; int n = 2; perm('' up n n); result(); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
# Python code implementation class FirstHalf: def __init__(self data sum): self.data = data self.sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString(s): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range(len(s)): sum += ord(s[i]) - ord('0') return sum def perm(p bin level n): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0: # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString(p) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.append(FirstHalf(p sum)) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map: map[sum] = [] map[sum].append(p) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range(len(bin)): perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n) def result(): i = 0 for j in range(len(firstHalf)): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf[j].sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map[sum] for k in range(len(secondHalf)): # append first and second half and print print(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' ' end='') # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if(i % 6 == 0): print('n') up = ['0' '1'] n = 2 perm('' up n n) result() # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class FirstHalf { public string data; public int sum; public FirstHalf(string data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary<int List<string>> mp = new Dictionary<int List<string>>(); // first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new List<FirstHalf>(); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString(string s) { int sum = 0; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach (char c in s) { sum += (c - '0'); } return sum; } static void perm(string p char[] bin int level int n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if (level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.Add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if (mp.ContainsKey(sum)) { mp[sum].Add(p); } else { mp.Add(sum new List<string> { p }); } return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = bin[i]; perm(p + c bin level - 1 n); } } static void result() { int i = 0; foreach (FirstHalf first in firstHalf) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List<string> secondHalf = mp[sum]; foreach (string second in secondHalf) { // append first and second half and print Console.Write(first.data + second + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if (i % 6 == 0) Console.WriteLine(); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { char[] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2; string x = ''; perm(x up n n); result(); } }
class FirstHalf { constructor(data sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map(); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString(s) { let sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { sum += s.charCodeAt(i) - '0'.charCodeAt(0); } return sum; } function perm(p bin level n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if(level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.push(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if(!map.has(sum)) map.set(sum []); map.get(sum).push(p); return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(let i = 0; i < bin.length; i++) { perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n); } } function result() { let i = 0; for(let j = 0; j < firstHalf.length; j++) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf[j].sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(let k = 0; k < secondHalf.length; k++) { // append first and second half and print process.stdout.write(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) process.stdout.write('n'); } } } const up = ['0' '1']; const n = 2; perm('' up n n); result();
Produzione
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algoritmo:
1. Genera tutte le permutazioni binarie di dimensione n
2. Calcola la somma dei bit di ciascuna permutazione e ricordala per la seconda metà
[ad es: per n=2 ricorda che ci sono due stringhe con somma = 1 cioè '01' '10' ]
3. Iterare tutte le permutazioni generate e per ciascuna di esse aggiungere la seconda metà in base alla somma dei bit
Analisi della complessità temporale:
if else istruzione java
somma delle stringhe() = O(N): attraversa ogni bit e aggiungilo alla somma
permanente() = O(2N* N)
2N * N : generiamo tutte le permutazioni di bit binari di dimensione N e troviamo la somma dei bit per ciascuna permutazione
risultato() = O((2N) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2N: iteriamo attraverso tutte le possibili permutazioni della dimensione N (primo tempo)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2: (dimensione massima della seconda metà): spiegazione di seguito:
Giochi iMessage con Android
prendiamo come esempio N = 4:
//Assomiglia a Hash-Map
0 -> [0000] ..............................(dimensione elenco: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................(dimensione elenco: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................(dimensione elenco: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................(dimensione elenco: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ..............................(dimensione elenco: 4C4 = 1)
Osserviamo qui che ciascuna lista ha una dimensione di N choose Key che sarà massima in N choose N/2
Dal momento che stiamo ripetendo tutti e 2Npermutazioni e aggiunta della seconda metà dalla mappa. La mappa ha l'elenco di dimensioni massime nella posizione N/2.
Il caso peggiore si verifica nella posizione N/2 dove dobbiamo attraversare NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2permutazioni.
Complessità temporale: O(2N*N!/(N/2)!2)
Spazio ausiliario: O(2N) perché memorizziamo tutte le permutazioni di stringhe binarie di dimensione N
