Date due stringhe, S1 E S2 , il compito è trovare la lunghezza della sottosequenza comune più lunga, ovvero la sottosequenza più lunga presente in entrambe le stringhe.
UN sottosequenza comune più lunga (LCS) è definita come la sottosequenza più lunga che è comune a tutte le sequenze di input date.
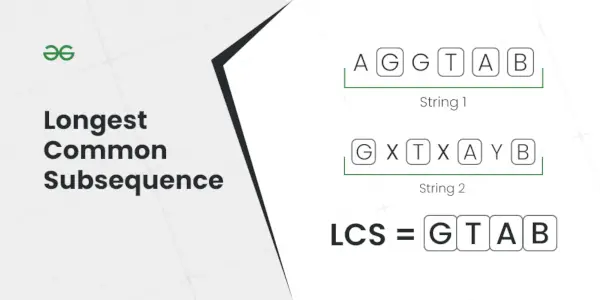
Sottosequenza comune più lunga
scarica video da youtube con vlc
Esempi:
Pratica consigliata Sottosequenza comune più lunga Provalo!Ingresso: S1 = ABC, S2 = ACD
Produzione: 2
Spiegazione: La sottosequenza più lunga presente in entrambe le stringhe è AC.Ingresso: S1 = AGGTAB, S2 = GXTXAYB
Produzione: 4
Spiegazione: La sottosequenza comune più lunga è GTAB.Ingresso: S1 = ABC, S2 = CBA
Produzione: 1
Spiegazione: Esistono tre sottosequenze comuni di lunghezza 1, A, B e C e nessuna sottosequenza comune di lunghezza superiore a 1.Ingresso: S1 = XYZW, S2 = XYWZ
Produzione: 3
Spiegazione: Esistono due sottosequenze comuni di lunghezza 3 XYZ e XYW e nessuna sottosequenza comune. di lunghezza superiore a 3.
Sottosequenza comune più lunga (LCS) utilizzando la ricorsione:
Genera tutte le possibili sottosequenze e trova tra queste la più lunga presente in entrambe le stringhe utilizzando Segui i passaggi seguenti per implementare l'idea:
- Creare una funzione ricorsiva [diciamo lcs() ].
- Verificare la relazione tra i primi caratteri delle stringhe non ancora elaborate.
- A seconda della relazione, chiama la successiva funzione ricorsiva come menzionato sopra.
- Restituisce la lunghezza della LCS ricevuta come risposta.
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione dell'approccio ricorsivo:
C++C// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra>Giava// A Naive recursive implementation // of LCS problem #include int max(int a, int b); // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int i, int j) // Utility function to get max of // 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un:b; } // Codice driver int main() { char S1[] = 'BD'; carattere S2[] = 'ABCD'; int m = strlen(S1); int n = strlen(S2); int i = 0, j = 0; // Chiamata alla funzione printf('La lunghezza di LCS è %d', lcs(S1, S2, i, j)); restituire 0; }>Pitone// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem in java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) n == 0) return 0; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1); else return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n)); // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un: b; } // Codice driver public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Stringa S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Stringa S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.lunghezza(); int n = S2.lunghezza(); System.out.println('La lunghezza di LCS è' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Questo codice è stato fornito da Saket Kumar>C## A Naive recursive Python implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): if m == 0 or n == 0: return 0 elif X[m-1] == Y[n-1]: return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1) else: return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, len(S1), len(S2)))>Javascript// C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) if (m == 0 // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un:b; } // Codice driver public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Stringa S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Lunghezza; int n = S2.Lunghezza; Console.Write('La lunghezza di LCS è' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Questo codice è stato fornito da Sam007>PHP>
ProduzioneLength of LCS is 4>Complessità temporale: O(2m+n)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)archivio espertoUtilizzo della sottosequenza comune più lunga (LCS). Memoizzazione :
1. Sottostruttura ottimale:
Vedi per risolvere la struttura di L(X[0, 1, . . ., m-1], Y[0, 1, . . . , n-1]) stiamo prendendo l'aiuto delle sottostrutture di X[0 , 1, …, m-2], Y[0, 1,…, n-2], a seconda della situazione (cioè utilizzandoli in modo ottimale) per trovare la soluzione del tutto.
2. Sottoproblemi sovrapposti:
Se usiamo l'approccio ricorsivo di cui sopra per le stringhe B.D E ABCD , otterremo un albero di ricorsione parziale come mostrato di seguito. Qui possiamo vedere che il sottoproblema L(BD, ABCD) viene calcolato più di una volta. Se si considera l'albero totale, ci saranno diversi sottoproblemi sovrapposti.
L(AXYT, AYZX)
/
L(AXY, AYZX) L(AXYT, AYZ)
//
L(AX, AYZX) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXYT, AY)Approccio: A causa della presenza di queste due proprietà possiamo utilizzare la programmazione dinamica o la memoizzazione per risolvere il problema. Di seguito è riportato l'approccio per la soluzione utilizzando la ricorsione.
- Creare una funzione ricorsiva. Crea anche un array 2D per memorizzare il risultato di uno stato univoco.
- Durante la chiamata ricorsiva, se lo stesso stato viene chiamato più di una volta, possiamo restituire direttamente la risposta memorizzata per quello stato invece di eseguire nuovamente il calcolo.
Di seguito è riportata l’implementazione dell’approccio di cui sopra:
data locale JavaC++Giava// A Top-Down DP implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int m, int n, vector>& dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } // Codice driver int main() { char X[] = 'AGGTAB'; carattere Y[] = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = strlen(X); int n = strlen(Y); vettore > dp(m + 1, vettore (n+1, -1)); cout<< 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp); return 0; }> Pitone/*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.*; class GFG { // A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n, int[][] dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (dp[m][n] != -1) return dp[m][n]; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) { dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); return dp[m][n]; } dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); return dp[m][n]; } // Drivers code public static void main(String args[]) { String X = 'AGGTAB'; String Y = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = X.length(); int n = Y.length(); int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) { dp[i][j] = -1; } } System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C## A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem # Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] def lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp): if (m == 0 or n == 0): return 0 if (dp[m][n] != -1): return dp[m][n] if X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]: dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp) return dp[m][n] dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)) return dp[m][n] # Driver code X = 'AGGTAB' Y = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(X) n = len(Y) dp = [[-1 for i in range(n + 1)]for j in range(m + 1)] print(f'Length of LCS is {lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)}') # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>Javascript/* C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */ using System; class GFG { /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ static int lcs(char[] X, char[] Y, int m, int n, int[, ] L) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (L[m, n] != -1) return L[m, n]; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) { L[m, n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, L); return L[m, n]; } L[m, n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, L), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, L)); return L[m, n]; } /* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */ static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un: b; } public static void Main() { String s1 = 'AGGTAB'; Stringa s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; char[] X = s1.ToCharArray(); char[] Y = s2.ToCharArray(); int m = X.Lunghezza; int n = Y.Lunghezza; int[, ] L = nuovo int[m + 1, n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i<= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { L[i, j] = -1; } } Console.Write('Length of LCS is' + ' ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, L)); } } // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>/* A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem */ /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ function lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } /* Driver code */ let X = 'AGGTAB'; let Y = 'GXTXAYB'; let m = X.length; let n = Y.length; let dp = new Array(m + 1); for(let i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { dp[i] = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1); } console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>
ProduzioneLength of LCS is 4>Complessità temporale: O(m * n) dove m e n sono le lunghezze delle stringhe.
Spazio ausiliario: O(m * n) Qui lo spazio dello stack ricorsivo viene ignorato.Sottosequenza comune più lunga (LCS) utilizzando il metodo bottom-up (tabulazione):
Possiamo utilizzare i seguenti passaggi per implementare l'approccio di programmazione dinamica per LCS.
- Crea una matrice 2D dp[][] con righe e colonne pari alla lunghezza di ciascuna stringa di input più 1 [il numero di righe indica gli indici di S1 e le colonne indicano gli indici di S2 ].
- Inizializza la prima riga e colonna dell'array dp su 0.
- Scorrere le righe dell'array dp, a partire da 1 (ad esempio utilizzando iterator io ).
- Per ciascuno io , ripetere tutte le colonne da j = 1 a n :
- Se S1[i-1] è uguale a S2[j-1] , imposta l'elemento corrente dell'array dp sul valore dell'elemento su ( dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 ).
- Altrimenti, imposta l'elemento corrente dell'array dp sul valore massimo di dp[i-1][j] E dp[i][j-1] .
- Dopo i cicli nidificati, l'ultimo elemento dell'array dp conterrà la lunghezza dell'LCS.
Vedere l'illustrazione seguente per una migliore comprensione:
Illustrazione:
Diciamo che le corde lo sono S1 = AGGTAB E S2 = GXTXAYB .
Primo passo: Inizialmente crea una matrice 2D (diciamo dp[][]) di dimensione 8 x 7 la cui prima riga e prima colonna sono riempite con 0.
Creazione della tabella DP
Secondo passo: Traversa per i = 1. Quando j diventa 5, S1[0] e S2[4] sono uguali. Quindi il dp[][] viene aggiornato. Per gli altri elementi assumere il massimo tra dp[i-1][j] e dp[i][j-1]. (In questo caso, se entrambi i valori sono uguali, abbiamo utilizzato le frecce per le righe precedenti).
Compilando la riga n. 1
es5 contro es6Terzo passo: Mentre attraversato per i = 2, S1[1] e S2[0] sono gli stessi (entrambi sono 'G'). Quindi il valore dp in quella cella viene aggiornato. Il resto degli elementi vengono aggiornati secondo le condizioni.
Compilando la riga n. 2
Quarto passo: Per i = 3, S1[2] e S2[0] sono ancora la stessa cosa. Gli aggiornamenti sono i seguenti.
Compilazione della riga n. 3
Quinto passo: Per i = 4, possiamo vedere che S1[3] e S2[2] sono la stessa cosa. Quindi dp[4][3] aggiornato come dp[3][2] + 1 = 2.
Riempimento della riga 4
Sesto passo: Qui possiamo vedere che per i = 5 e j = 5 i valori di S1[4] e S2[4] sono gli stessi (cioè entrambi sono 'A'). Quindi dp[5][5] viene aggiornato di conseguenza e diventa 3.
cena contro cenaRiempimento della riga 5
Passo finale: Per i = 6, vedere gli ultimi caratteri di entrambe le stringhe sono uguali (sono 'B'). Pertanto il valore di dp[6][7] diventa 4.
Riempiendo l'ultima riga
Quindi otteniamo la lunghezza massima della sottosequenza comune come 4 .
Di seguito è riportata un'implementazione tabellata per il problema LCS.
C++Giava// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) { // Initializing a matrix of size // (m+1)*(n+1) int L[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. Note that // L[i][j] contains length of LCS of // X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) if (i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains length of LCS // for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n]; } // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; }>Pitone// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int L[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up // fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS // of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X.charAt(i - 1) == Y.charAt(j - 1)) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } return L[m][n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un:b; } public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Stringa S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Stringa S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.lunghezza(); int n = S2.lunghezza(); System.out.println('La lunghezza di LCS è' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Questo codice è stato fornito da Saket Kumar>C## Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): # Declaring the array for storing the dp values L = [[None]*(n+1) for i in range(m+1)] # Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion # Note: L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] # and Y[0..j-1] for i in range(m+1): for j in range(n+1): if i == 0 or j == 0: L[i][j] = 0 elif X[i-1] == Y[j-1]: L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1]+1 else: L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1]) # L[m][n] contains the length of LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n] # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(S1) n = len(S2) print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, m, n)) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)>Javascript// Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int[, ] L = new int[m + 1, n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. // Note that L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i, j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i, j] = L[i - 1, j - 1] + 1; else L[i, j] = max(L[i - 1, j], L[i, j - 1]); } return L[m, n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>B) ? un: b; } // Codice driver public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Stringa S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Lunghezza; int n = S2.Lunghezza; Console.Write('La lunghezza di LCS è' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Questo codice è stato fornito da Sam007>PHP// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem // Utility function to get max of 2 integers function max(a, b) { if (a>b) restituire a; altrimenti restituisce b; } // Restituisce la lunghezza di LCS per X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] funzione lcs(X, Y, m, n) { var L = new Array(m + 1); for(var i = 0; i< L.length; i++) { L[i] = new Array(n + 1); } var i, j; /* Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] */ for(i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for(j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } /* L[m][n] contains length of LCS for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] */ return L[m][n]; } // Driver code var S1 = 'AGGTAB'; var S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; var m = S1.length; var n = S2.length; console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>// Dynamic Programming C# // implementation of LCS problem function lcs($X , $Y, $m, $n) { // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion . // Note: L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for ($i = 0; $i <= $m; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j <= $n; $j++) if ($i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains the length of // LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return $L[$m][$n]; } // Driver Code $S1 = 'AGGTAB'; $S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; $m = strlen($S1); $n = strlen($S2) ; echo 'Length of LCS is '; echo lcs($S1, $S2, $m, $n); // This code is contributed // by Shivi_Aggarwal ?>>
ProduzioneLength of LCS is 4>Complessità temporale: O(m * n) che è molto migliore della complessità temporale nel caso peggiore dell'implementazione Naive Recursive.
Spazio ausiliario: O(m * n) perché l'algoritmo utilizza un array di dimensione (m+1)*(n+1) per memorizzare la lunghezza delle sottostringhe comuni.Sottosequenza comune più lunga (LCS) utilizzando il metodo Bottom-Up (ottimizzazione dello spazio):
- Nell'approccio di tabulazione di cui sopra stiamo usando L[i-1][j] e L[i][j] ecc., qui L[i-1] si riferisce alla riga precedente della matrice L e L[i] si riferisce a la riga corrente.
- Possiamo ottimizzare lo spazio utilizzando due vettori, uno è precedente e l'altro è corrente.
- Quando il ciclo for interno termina, stiamo inizializzando precedente uguale a corrente.
Di seguito l'implementazione:
C++Giava// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; int longestCommonSubsequence(string& text1, string& text2) { int n = text1.size(); int m = text2.size(); // initializing 2 vectors of size m vectorprev(m + 1, 0), cur(m + 1, 0); for (int idx2 = 0; idx2< m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2); return 0; }> Pitone// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.Arrays; public class GFG { public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(); int m = text2.length(); // Initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If matching if (text1.charAt(idx1 - 1) == text2.charAt(idx2 - 1)) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // Not matching else cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = Arrays.copyOf(cur, m + 1); } return cur[m]; } public static void main(String[] args) { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; String S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>C#def longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2): n = len(text1) m = len(text2) # Initializing two lists of size m prev = [0] * (m + 1) cur = [0] * (m + 1) for idx1 in range(1, n + 1): for idx2 in range(1, m + 1): # If characters are matching if text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]: cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1] else: # If characters are not matching cur[idx2] = max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]) prev = cur.copy() return cur[m] if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' # Function call print('Length of LCS is', longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)) # This code is contributed by Rishabh Mathur>Javascriptusing System; class Program { static int LongestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n = text1.Length; int m = text2.Length; // initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + Math.Max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } static void Main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call Console.WriteLine('Length of LCS is ' + LongestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>function longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2) { const n = text1.length; const m = text2.length; // Initializing two arrays of size m let prev = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); let cur = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); for (let idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { cur[idx2] = 0; } for (let idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (let idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If characters match if (text1[idx1 - 1] === text2[idx2 - 1]) { cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; } // If characters don't match else { cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } } // Update the 'prev' array prev = [...cur]; } return cur[m]; } // Main function function main() { const S1 = 'AGGTAB'; const S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call console.log('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } // Call the main function main();>
ProduzioneLength of LCS is 4>Complessità temporale: O(m*n), che rimane lo stesso.
Spazio ausiliario: O(m) perché l'algoritmo utilizza due array di dimensione m.







