Data una carta rettangolare di dimensioni unxb . Il compito è tagliare l'intero foglio nel formato minimo numero di piazza pezzi. Possiamo scegliere pezzi quadrati di qualsiasi dimensione ma devono essere tagliati senza sovrapporsi o lasciare spazio aggiuntivo .
Esempi:
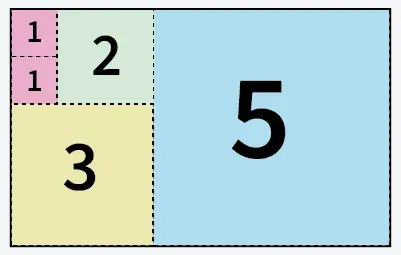
Ingresso: a = 5 b = 8
5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 5 X 8
Produzione: 5
Spiegazione: Possiamo tagliare la carta in 5 quadrati: 1 quadrato di misura 5x5 1 quadrato di misura 3x3 1 quadrato di misura 2x2 e 2 quadrati di misura 1x1.Ingresso: a = 13 b = 11
6 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 13 X 11
Produzione: 6
Spiegazione: Possiamo tagliare la carta in 6 quadrati: 1 quadrato di misura 7x7 1 quadrato di misura 6x6 1 quadrato di misura 5x5 2 quadrati di misura 4x4 e 1 quadrato di misura 1x1.inserendo la stringa in JavaIngresso: a = 6 b = 7
5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 6 X 7
Produzione: 5
Spiegazione: Possiamo tagliare la carta in 5 quadrati: 1 quadrato di misura 4x4 2 quadrati di misura 3x3 e 2 quadrati di misura 3x3.scanner java
Sommario
- [Approccio Errato 1] Usare la Tecnica Greedy
- [Approccio Errato 2] Utilizzo della Programmazione Dinamica
- [Approccio corretto] Utilizzo di DFS e programmazione dinamica
[Approccio Errato 1] Usare la Tecnica Greedy
A prima vista potrebbe sembrare che il problema possa essere facilmente risolto tagliando prima il quadrato più grande possibile dalla carta, poi tagliando il quadrato più grande dalla carta rimanente e così via fino a tagliare l'intera carta. Ma questa soluzione non è corretta.
Perché l'approccio goloso non funziona?
Considera un foglio di formato 6x7 poi se proviamo a tagliare avidamente la carta otterremo 7 quadrati: 1 quadrato di dimensione 6x6 e 6 quadrati di dimensione 1x1 mentre la soluzione corretta è: 5. Quindi l'approccio avido non funzionerà.
[Approccio Errato 2] Utilizzo della Programmazione Dinamica
Programmazione dinamica con tagli verticali o orizzontali: Un'altra soluzione che potrebbe sembrare corretta è l'utilizzo Programmazione dinamica . Possiamo mantenere una tabella dp[][] tale che dp[i][j] = numero minimo di quadrati ritagliabili dalla carta di formato io x j . Quindi per la carta di formato axb
- Possiamo provare a tagliarlo lungo ogni riga: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) dove k può essere compreso nell'intervallo [1 i - 1].
- Possiamo provare a tagliarlo lungo ciascuna colonna: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) dove k può essere compreso nell'intervallo [1 j - 1].
Alla fine la risposta sarà il minimo dei tagli. Ma anche questa soluzione è sbagliata.
Perché tagliare verticalmente o orizzontalmente con l'approccio di programmazione dinamica non funziona?
Questo non funzionerà perché presupponiamo che un taglio verticale o orizzontale dividerà sempre il rettangolo in due parti. Considera un foglio di formato 13x11 quindi se proviamo a tagliare la carta utilizzando l'approccio DP otterremo 8 quadrati ma la risposta corretta (come mostrato negli esempi) è 6. Quindi la programmazione dinamica non funzionerà.
[Approccio corretto] Utilizzo di DFS e programmazione dinamica
C++IL idea è tagliare l'intera carta usando DFS In dal basso verso l'alto maniera. Ad ogni passaggio, trova l'angolo in basso a sinistra del foglio e prova a tagliare quadrati di tutte le dimensioni possibili da quell'angolo. Dopo aver tagliato nuovamente un quadrato, trova l'angolo inferiore sinistro della carta rimanente per tagliare quadrati di tutte le dimensioni possibili e così via. Ma se provassimo tutti i possibili tagli dall'angolo inferiore sinistro di ogni possibile formato carta, sarebbe del tutto inefficiente. Possiamo ottimizzarlo utilizzando Programmazione dinamica per memorizzare i tagli minimi per ogni possibile formato carta.
Per identificare in modo univoco qualsiasi dimensione del foglio possiamo mantenere un array remSq[] tale che remSq[i] memorizzi il numero di quadrati rimanenti di dimensione 1x1 nell'i-esima colonna del foglio. Quindi per un foglio di dimensioni 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Anche per trovare l'angolo in basso a sinistra troveremo il primo indice avente il massimo dei quadrati rimanenti. Quindi possiamo eseguire l'hashing del valore dell'array remSq[] per trovare una chiave univoca per tutti i possibili valori dell'array remSq[].
test delle prestazioni
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Produzione
6
Complessità temporale: O(a^b) per ciascuna delle b colonne possiamo avere un quadrato.
Spazio ausiliario: O(a^b) grazie alla memorizzazione di ogni stato univoco.

 5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 5 X 8
5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 5 X 8 6 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 13 X 11
6 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 13 X 11 5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 6 X 7
5 quadrati ritagliati da carta di formato 6 X 7