Il processo decisionale è l’aspetto più importante di quasi tutti i linguaggi di programmazione. Come suggerisce il nome, il processo decisionale ci consente di eseguire un particolare blocco di codice per una particolare decisione. Qui si decide sulla validità delle condizioni particolari. Il controllo delle condizioni è la spina dorsale del processo decisionale.
come inizializzare un array in Java
In Python, il processo decisionale viene eseguito dalle seguenti istruzioni.
| Dichiarazione | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| Se Dichiarazione | L'istruzione if viene utilizzata per testare una condizione specifica. Se la condizione è vera, verrà eseguito un blocco di codice (if-block). |
| Se - altrimenti Dichiarazione | L'istruzione if-else è simile all'istruzione if tranne per il fatto che fornisce anche il blocco del codice per il caso falso della condizione da verificare. Se la condizione fornita nell'istruzione if è falsa, verrà eseguita l'istruzione else. |
| Nidificata se istruzione | Le istruzioni if nidificate ci consentono di utilizzare if ? istruzione else all'interno di un'istruzione if esterna. |
Rientro in Python
Per facilità di programmazione e per raggiungere la semplicità, Python non consente l'uso di parentesi per il codice a livello di blocco. In Python, il rientro viene utilizzato per dichiarare un blocco. Se due istruzioni si trovano allo stesso livello di rientro, allora fanno parte dello stesso blocco.
Generalmente, vengono forniti quattro spazi per rientrare le istruzioni che rappresentano una tipica quantità di rientro in Python.
Il rientro è la parte più utilizzata del linguaggio Python poiché dichiara il blocco di codice. Tutte le istruzioni di un blocco si intendono allo stesso livello di indentazione. Vedremo come avviene l'effettivo rientro nel processo decisionale e altre cose in Python.
L'istruzione if
L'istruzione if viene utilizzata per testare una particolare condizione e, se la condizione è vera, esegue un blocco di codice noto come if-block. La condizione dell'istruzione if può essere qualsiasi espressione logica valida che può essere valutata come vera o falsa.
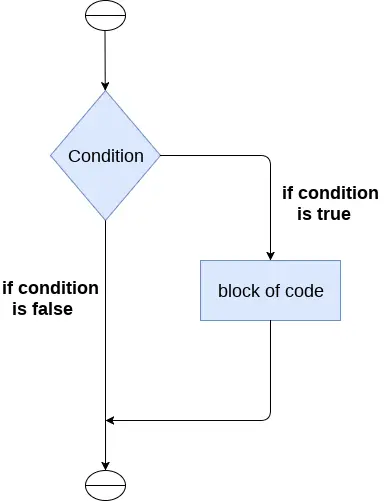
La sintassi dell'istruzione if è riportata di seguito.
Algoritmo dfs
if expression: statement
Esempio 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Produzione:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Esempio 2: Programma per stampare il più grande dei tre numeri.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Produzione:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
L'istruzione if-else
L'istruzione if-else fornisce un blocco else combinato con l'istruzione if che viene eseguito nel caso falso della condizione.
Se la condizione è vera, viene eseguito il blocco if. Altrimenti viene eseguito il blocco else.

La sintassi dell'istruzione if-else è riportata di seguito.
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Esempio 1: Programma per verificare se una persona ha diritto di voto o meno.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Produzione:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Esempio 2: programma per verificare se un numero è pari o meno.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Produzione:
b+ alberi
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
L'enunciato elif
L'istruzione elif ci consente di verificare più condizioni ed eseguire il blocco specifico di istruzioni a seconda della vera condizione tra di loro. Possiamo avere un numero qualsiasi di istruzioni elif nel nostro programma a seconda delle nostre necessità. Tuttavia, l'utilizzo di elif è facoltativo.
L'istruzione elif funziona come un'istruzione ladder if-else-if in C. Deve essere seguita da un'istruzione if.
La sintassi dell'istruzione elif è riportata di seguito.
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Esempio 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Produzione:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Esempio 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 