La funzione Totiente di Eulero Φ(n) per un input n è il conteggio dei numeri in {1, 2, 3, …, n-1} che sono primi rispetto a n, cioè i numeri il cui MCD (massimo comun divisore) con n è 1.
Esempi:
Φ(1) = 1
mcd(1, 1) è 1
Φ(2) = 1
mcd(1, 2) è 1, ma mcd(2, 2) è 2.
Φ(3) = 2
mcd(1, 3) è 1 e mcd(2, 3) è 1
Φ(4) = 2
mcd(1, 4) è 1 e mcd(3, 4) è 1
Φ(5) = 4
mcd(1, 5) è 1, mcd(2, 5) è 1,
mcd(3, 5) è 1 e mcd(4, 5) è 1
Φ(6) = 2
mcd(1, 6) è 1 e mcd(5, 6) è 1,
Pratica consigliata Funzione Eulero Totient Provalo!
Come calcolare Φ(n) per un input n?
UN soluzione semplice consiste nell'iterare tutti i numeri da 1 a n-1 e contare i numeri con mcd con n come 1. Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione del metodo semplice per calcolare la funzione Totient di Eulero per un numero intero di input n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Giava // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Produzione
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
per l'array di stringhe Java
Il codice precedente chiama la funzione gcd O(n) volte. La complessità temporale della funzione mcd è O(h) dove h è il numero di cifre in un numero più piccolo di due numeri dati. Pertanto, un limite superiore al complessità temporale della soluzione di cui sopra è O(N^2 log N) [Come Φ può esserci al massimo Log10n cifre in tutti i numeri da 1 a n]
Spazio ausiliario: O(logN)
Di seguito è riportato un Soluzione migliore . L’idea si basa sulla formula del prodotto di Eulero che afferma che il valore delle funzioni totali è inferiore al prodotto dei fattori primi complessivi p di n.
La formula sostanzialmente dice che il valore di Φ(n) è uguale a n moltiplicato per il sottoprodotto di (1 – 1/p) per tutti i fattori primi p di n. Ad esempio il valore di Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Possiamo trovare tutti i fattori primi utilizzando l'idea utilizzata in Questo inviare.
1) Inizializza: risultato = n
2) Esegui un ciclo da 'p' = 2 a sqrt(n), procedi per ogni 'p'.
a) Se p divide n, allora
Imposta: risultato = risultato * (1.0 - (1.0 / (float) p));
Dividi tutte le occorrenze di p in n.
3) Restituisci il risultato
Di seguito è riportata l’implementazione della formula del prodotto di Eulero.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return (int)result; } // Codice del driver int main() { int n; per(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return (int)result; } // Programma driver per testare la funzione precedente int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Giava // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return (int)result; } // Programma driver per testare la funzione precedente public static void main(String args[]) { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : risultato -= risultato // n #Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n #se n è un numero primo return int(risultato) # Driver programma per testare la funzione precedente per n in range(1, 11) : print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Questo codice è fornito # da Nikita Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return (int)result; } // Codice driver public static void Main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return parseInt(risultato); } // Codice driver per (let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $risultato -= $risultato / $n; //Poiché nell'insieme {1,2,....,n-1}, tutti i numeri sono primi tra loro con n //se n è un numero primo return intval($risultato); } // Codice driver per ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Produzione
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Complessità temporale: O(Φ n log n)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
Possiamo evitare i calcoli in virgola mobile nel metodo sopra. L'idea è di contare tutti i fattori primi e i loro multipli e sottrarre questo conteggio da n per ottenere il valore della funzione totale (i fattori primi e i multipli di fattori primi non avranno mcd pari a 1)
1) Inizializza il risultato come n
2) Consideriamo ogni numero 'p' (dove 'p' varia da 2 a Φ(n)).
Se p divide n, allora fai quanto segue
a) Sottrarre tutti i multipli di p da 1 a n [tutti i multipli di p
avrà mcd più di 1 (almeno p) con n]
b) Aggiorna n dividendolo ripetutamente per p.
3) Se n ridotto è maggiore di 1, rimuovi tutti i multipli
di n dal risultato.
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione dell'algoritmo di cui sopra.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; risultato restituito; } // Codice del driver int main() { int n; per(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; risultato restituito; } // Programma driver per testare la funzione precedente int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Giava // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; risultato restituito; } // Codice driver public static void main (String[] args) { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): risultato -= int(risultato / n); risultato restituito; # Codice driver per n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Questo codice è stato contribuito # da mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= risultato / n; risultato restituito; } // Codice driver static public void Main () { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) risultato -= parseInt(risultato / n); risultato restituito; } // Codice driver per (let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $risultato -= (int)$risultato / $n; restituire $risultato; } // Codice driver per ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Produzione
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Complessità temporale: O(Φ n log n)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
Facciamo un esempio per comprendere l'algoritmo di cui sopra.
dhanashree verma
n = 10.
Inizializza: risultato = 10
2 è un fattore primo, quindi n = n/i = 5, risultato = 5
3 non è un fattore primo.
Il ciclo for si ferma dopo 3 poiché 4*4 non è inferiore o uguale
a 10.
Dopo il ciclo for, risultato = 5, n = 5
Poiché n> 1, risultato = risultato - risultato/n = 4
Alcune proprietà interessanti della funzione toziente di Eulero
1) Per un numero primo pag ,
Prova :
Esempi:
2) Per due numeri primi a e b
Prova :
Esempi:
3) Per un numero primo p ,
Prova :
Esempi:
4) Per due numeri a e b
Caso speciale: mcd(a, b) = 1
attore amrita rao
Esempi:
Caso speciale :
5) La somma dei valori delle funzioni totali di tutti i divisori di n è uguale a n.
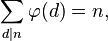
Esempi:
n = 6
fattori = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) La caratteristica più famosa e importante è espressa in Il teorema di Eulero :
Il teorema afferma che se n e a sono coprimi
(o relativamente primi) interi positivi, quindi
UNΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
IL Crittosistema RSA si basa su questo teorema:
Nel caso particolare in cui m è primo, ad esempio p, il teorema di Eulero diventa il cosiddetto Il piccolo teorema di Fermat :
UNp-1Φ 1 (contro p)
7) Il numero di generatori di un gruppo ciclico finito con addizione modulo n è Φ(n) .
Articolo correlato:
Funzione Totient di Eulero per tutti i numeri minori o uguali a n
Funzione Totient di Eulero ottimizzata per valutazioni multiple
Riferimenti:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
