Introduzione:
Gli abbreviatori URL sono un esempio di hashing poiché mappano URL di grandi dimensioni in dimensioni ridotte
Alcuni esempi di funzioni hash:
- chiave % numero di bucket
- Valore ASCII del carattere * PrimeNumberX. Dove x = 1, 2, 3….n
- Puoi creare la tua funzione hash, ma dovrebbe essere una buona funzione hash che dia meno numero di collisioni.
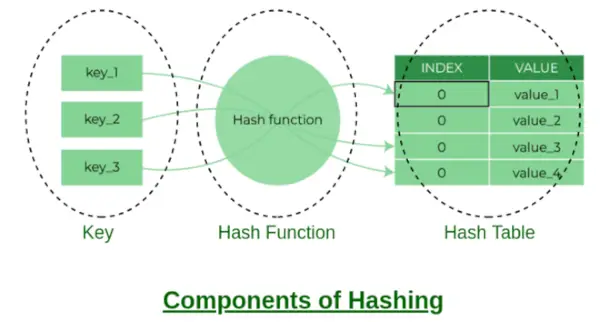
Componenti dell'hashing
Indice del segmento:
Il valore restituito dalla funzione Hash è l'indice del bucket per una chiave in un metodo di concatenamento separato. Ogni indice nell'array è chiamato bucket poiché è un bucket di un elenco collegato.
Ripeto:
Il rehashing è un concetto che riduce la collisione quando gli elementi vengono aumentati nella tabella hash corrente. Creerà un nuovo array di dimensioni raddoppiate e vi copierà gli elementi dell'array precedente ed è come il funzionamento interno del vettore in C++. Ovviamente, la funzione Hash dovrebbe essere dinamica in quanto dovrebbe riflettere alcuni cambiamenti quando la capacità viene aumentata. La funzione hash include la capacità della tabella hash al suo interno, pertanto, mentre copia i valori chiave dalla precedente funzione hash dell'array fornisce indici di bucket diversi poiché dipende dalla capacità (bucket) della tabella hash. Generalmente, quando il valore del fattore di carico è maggiore di 0,5 vengono eseguiti dei ripescaggi.
- Raddoppia la dimensione dell'array.
- Copia gli elementi dell'array precedente nel nuovo array. Usiamo la funzione hash mentre copiamo nuovamente ciascun nodo in un nuovo array, quindi ridurrà la collisione.
- Elimina l'array precedente dalla memoria e punta il puntatore dell'array interno della mappa hash su questo nuovo array.
- Generalmente, Load Factor = numero di elementi nella Hash Map/numero totale di bucket (capacità).
Collisione:
La collisione è la situazione in cui l'indice del bucket non è vuoto. Significa che in quell'indice del bucket è presente l'intestazione di una lista collegata. Abbiamo due o più valori associati allo stesso indice di bucket.
Principali funzioni del nostro programma
- Inserimento
- Ricerca
- Funzione hash
- Eliminare
- Ripassando
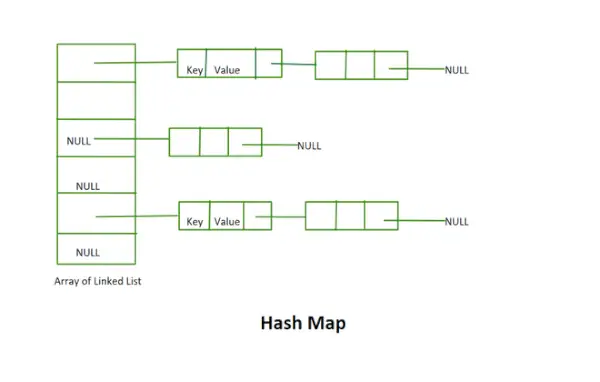
Mappa hash
Implementazione senza rehashing:
C
comando chown
java string.format
#include> #include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >node->chiave = chiave;> >node->valore = valore;> >node->successivo = NULL;> >return>;> };> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp)> {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacità = 100;> >mp->numElementi = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*)> >* mp->capacità);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacità)> >+ (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacità)> >% mp->capacità;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__)> >* (31 % __INT16_MAX__))> >% __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->next = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >return>;> }> void> delete> (>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[indicebucket];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->chiave) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->successivo = currNode->successivo;> >}> >free>(currNode);> >break>;> >}> >prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->successivo;> >}> >return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting the bucket index> >// for the given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >// Head of the linked list> >// present at bucket index> >struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[indicebucket];> >while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (bucketHead->chiave == chiave) {> >return> bucketHead->valore;> >}> >bucketHead = bucketHead->successivo;> >}> >// If no key found in the hashMap> >// equal to the given key> >char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> >errorMssg =>'Oops! No data found.
'>;> >return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> >// Initialize the value of mp> >struct> hashMap* mp> >= (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> >initializeHashMap(mp);> >insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> >insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> >insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> >insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> >insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> >// Key is not inserted> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> >printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> >// Deletion of key> >delete> (mp,>'decentBoy'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
C++
esempio di potatura alfa beta
#include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >node->chiave = chiave;> >node->valore = valore;> >node->successivo = NULL;> >return>;> }> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp) {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacità = 100;> >mp->numElementi = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*) * mp->capacità);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacità) + (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacità) % mp->capacità;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__) * (31 % __INT16_MAX__)) % __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->next = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >return>;> }> void> deleteKey(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[indicebucket];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->chiave) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->successivo = currNode->successivo;> }> free>(currNode);> break>;> }> prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->successivo;> >}> return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> // Getting the bucket index for the given key> int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> // Head of the linked list present at bucket index> struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[indicebucket];> while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> > >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (>strcmp>(bucketHead->chiave, chiave) == 0) {> >return> bucketHead->valore;> >}> > >bucketHead = bucketHead->successivo;> }> // If no key found in the hashMap equal to the given key> char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> strcpy>(errorMssg,>'Oops! No data found.
'>);> return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> // Initialize the value of mp> struct> hashMap* mp = (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> initializeHashMap(mp);> insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> // Key is not inserted> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> // Deletion of key> deleteKey(mp,>'decentBoy'>);> // Searching the deleted key> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> return> 0;> }> |
>
>Produzione
Manish Anjali Vartika Mayank techcodeview.com Oops! No data found. After deletion : Oops! No data found.>
Spiegazione:
- inserimento: inserisce la coppia chiave-valore all'inizio di un elenco collegato presente nell'indice del bucket specificato. hashFunction: fornisce l'indice del bucket per la chiave specificata. Nostro funzione hash = valore ASCII del carattere * numeroprimoX . Il numero primo nel nostro caso è 31 e il valore di x aumenta da 1 a n per i caratteri consecutivi in una chiave. eliminazione: elimina la coppia chiave-valore dalla tabella hash per la chiave specificata. Elimina il nodo dall'elenco collegato che contiene la coppia chiave-valore. Cerca: cerca il valore della chiave specificata.
- Questa implementazione non utilizza il concetto di rehashing. È un array di elenchi collegati di dimensioni fisse.
- Chiave e valore sono entrambi stringhe nell'esempio fornito.
Complessità temporale e complessità spaziale:
La complessità temporale delle operazioni di inserimento ed eliminazione della tabella hash è in media O (1). C'è qualche calcolo matematico che lo dimostra.
- Complessità temporale dell'inserimento: nel caso medio è costante. Nel peggiore dei casi, è lineare. Complessità temporale della ricerca: nel caso medio è costante. Nel peggiore dei casi, è lineare. Complessità temporale della cancellazione: nella media dei casi è costante. Nel peggiore dei casi, è lineare. Complessità spaziale: O(n) poiché ha n numero di elementi.
Articoli Correlati:
- Tecnica di gestione delle collisioni con concatenamento separato nell'hashing.
