UN Max-Heap è un albero binario completo in cui il valore in ciascun nodo interno è maggiore o uguale ai valori nei figli di quel nodo. Mappare gli elementi di un heap in un array è banale: se un nodo è memorizzato in un indice k, allora il suo figlio sinistro viene memorizzato in indice 2k+1 e il suo figlio destro all'indice 2k+2 .
Esempi di heap massimo:
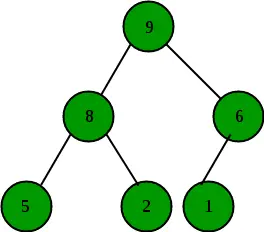
Come viene rappresentato Max Heap?
Un heap massimo è un albero binario completo. Un heap massimo è in genere rappresentato come un array. L'elemento radice sarà in Arr[0]. La tabella seguente mostra gli indici di altri nodi per l'i-esimo nodo, ovvero Arr[i]:
- Arr[(i-1)/2] Restituisce il nodo genitore.
- Arr[(2*i)+1] Restituisce il nodo figlio sinistro.
- Arr[(2*i)+2] Restituisce il nodo figlio destro.
Operazioni su Max Heap:
- getMax() : Restituisce l'elemento radice di Max Heap. La complessità temporale di questa operazione è O(1) .
- estrattoMax() : Rimuove l'elemento massimo da MaxHeap. La complessità temporale di questa operazione è O(log n) poiché questa operazione deve mantenere la proprietà heap (chiamando heapify()) dopo aver rimosso la radice.
- inserire() : L'inserimento di una nuova chiave richiede O(log n) tempo. Aggiungiamo una nuova chiave alla fine dell'albero. Se la nuova chiave è più piccola della chiave principale, non dobbiamo fare nulla. Altrimenti, dobbiamo risalire per correggere la proprietà heap violata.
Nota: Nell'implementazione seguente, eseguiamo l'indicizzazione dall'indice 1 per semplificare l'implementazione.
Pitone
stringa ti int
classe di oggetti in Java
# Python3 implementation of Max Heap> import> sys> class> MaxHeap:> >def> __init__(>self>, maxsize):> > >self>.maxsize>=> maxsize> >self>.size>=> 0> >self>.Heap>=> [>0>]>*> (>self>.maxsize>+> 1>)> >self>.Heap[>0>]>=> sys.maxsize> >self>.FRONT>=> 1> ># Function to return the position of> ># parent for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> parent(>self>, pos):> > >return> pos>/>/> 2> ># Function to return the position of> ># the left child for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> leftChild(>self>, pos):> > >return> 2> *> pos> ># Function to return the position of> ># the right child for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> rightChild(>self>, pos):> > >return> (>2> *> pos)>+> 1> ># Function that returns true if the passed> ># node is a leaf node> >def> isLeaf(>self>, pos):> > >if> pos>>=> (>self>.size>/>/>2>)>and> pos <>=> self>.size:> >return> True> >return> False> ># Function to swap two nodes of the heap> >def> swap(>self>, fpos, spos):> > >self>.Heap[fpos],>self>.Heap[spos]>=> (>self>.Heap[spos],> >self>.Heap[fpos])> ># Function to heapify the node at pos> >def> maxHeapify(>self>, pos):> ># If the node is a non-leaf node and smaller> ># than any of its child> >if> not> self>.isLeaf(pos):> >if> (>self>.Heap[pos] <>self>.Heap[>self>.leftChild(pos)]>or> >self>.Heap[pos] <>self>.Heap[>self>.rightChild(pos)]):> ># Swap with the left child and heapify> ># the left child> >if> (>self>.Heap[>self>.leftChild(pos)]>> >self>.Heap[>self>.rightChild(pos)]):> >self>.swap(pos,>self>.leftChild(pos))> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.leftChild(pos))> ># Swap with the right child and heapify> ># the right child> >else>:> >self>.swap(pos,>self>.rightChild(pos))> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.rightChild(pos))> ># Function to insert a node into the heap> >def> insert(>self>, element):> > >if> self>.size>>=> self>.maxsize:> >return> >self>.size>+>=> 1> >self>.Heap[>self>.size]>=> element> >current>=> self>.size> >while> (>self>.Heap[current]>> >self>.Heap[>self>.parent(current)]):> >self>.swap(current,>self>.parent(current))> >current>=> self>.parent(current)> ># Function to print the contents of the heap> >def> Print>(>self>):> > >for> i>in> range>(>1>, (>self>.size>/>/> 2>)>+> 1>):> >print>(>'PARENT : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[i])>+> >'LEFT CHILD : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[>2> *> i])>+> >'RIGHT CHILD : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[>2> *> i>+> 1>]))> ># Function to remove and return the maximum> ># element from the heap> >def> extractMax(>self>):> >popped>=> self>.Heap[>self>.FRONT]> >self>.Heap[>self>.FRONT]>=> self>.Heap[>self>.size]> >self>.size>->=> 1> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.FRONT)> > >return> popped> # Driver Code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > >print>(>'The maxHeap is '>)> > >maxHeap>=> MaxHeap(>15>)> >maxHeap.insert(>5>)> >maxHeap.insert(>3>)> >maxHeap.insert(>17>)> >maxHeap.insert(>10>)> >maxHeap.insert(>84>)> >maxHeap.insert(>19>)> >maxHeap.insert(>6>)> >maxHeap.insert(>22>)> >maxHeap.insert(>9>)> >maxHeap.>Print>()> > >print>(>'The Max val is '> +> str>(maxHeap.extractMax()))> |
>
>Produzione
quali mesi sono q1
The maxHeap is PARENT : 84LEFT CHILD : 22RIGHT CHILD : 19 PARENT : 22LEFT CHILD : 17RIGHT CHILD : 10 PARENT : 19LEFT CHILD : 5RIGHT CHILD : 6 PARENT : 17LEFT CHILD : 3RIGHT CHILD : 9 The Max val is 84>
Utilizzo delle funzioni della libreria:
Noi usiamo heapq classe per implementare Heap in Python. Per impostazione predefinita, Min Heap è implementato da questa classe. Ma moltiplichiamo ciascun valore per -1 in modo da poterlo utilizzare come MaxHeap.
Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate working of heapq> from> heapq>import> heappop, heappush, heapify> # Creating empty heap> heap>=> []> heapify(heap)> # Adding items to the heap using heappush> # function by multiplying them with -1> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 10>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 30>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 20>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 400>)> # printing the value of maximum element> print>(>'Head value of heap : '> +> str>(>->1> *> heap[>0>]))> # printing the elements of the heap> print>(>'The heap elements : '>)> for> i>in> heap:> >print>((>->1>*>i), end>=>' '>)> print>(>'
'>)> element>=> heappop(heap)> # printing the elements of the heap> print>(>'The heap elements : '>)> for> i>in> heap:> >print>(>->1> *> i, end>=> ' '>)> |
>
ordinamento in arraylist in Java
>Produzione
Head value of heap : 400 The heap elements : 400 30 20 10 The heap elements : 30 10 20>
Utilizzo delle funzioni di libreria con metodo dunder per numeri, stringhe, tuple, oggetti ecc
Noi usiamo heapq classe per implementare Heaps in Python. Per impostazione predefinita, Min Heap è implementato da questa classe.
Per implementare MaxHeap non limitandosi solo ai numeri ma a qualsiasi tipo di oggetto (stringa, tupla, oggetto ecc.) dovremmo
- Crea una classe Wrapper per l'elemento nell'elenco.
- Sostituisci il __lt__ metodo dunder per dare un risultato inverso.
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione del metodo qui menzionato.
Java che ordina un arraylist
Python3
'''> Python3 program to implement MaxHeap Operation> with built-in module heapq> for String, Numbers, Objects> '''> from> functools>import> total_ordering> import> heapq>|_+_| |
