Minimax è una sorta di algoritmo di backtracking utilizzato nel processo decisionale e nella teoria dei giochi per trovare la mossa ottimale per un giocatore, presupponendo che anche il tuo avversario giochi in modo ottimale. È ampiamente utilizzato nei giochi a turni per due giocatori come Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Scacchi, ecc.
In Minimax i due giocatori sono chiamati massimizzatore e minimizzatore. IL massimizzatore cerca di ottenere il punteggio più alto possibile mentre il minimizzatore cerca di fare il contrario e ottenere il punteggio più basso possibile.
Ad ogni stato della scheda è associato un valore. In un dato stato, se il massimizzatore ha il sopravvento, il punteggio del tabellone tenderà ad avere un valore positivo. Se il minimizzatore ha il sopravvento in quello stato della scheda, allora tenderà ad avere un valore negativo. I valori del tabellone sono calcolati mediante alcune euristiche uniche per ogni tipo di gioco.
Esempio:
Considera un gioco che ha 4 stati finali e i percorsi per raggiungere lo stato finale vanno dalla radice alle 4 foglie di un albero binario perfetto come mostrato di seguito. Supponiamo che tu sia il giocatore che massimizza e che tu abbia la prima possibilità di muoverti, cioè che tu sia alla radice e il tuo avversario al livello successivo. Quale mossa faresti come giocatore massimizzante considerando che anche il tuo avversario gioca in modo ottimale?
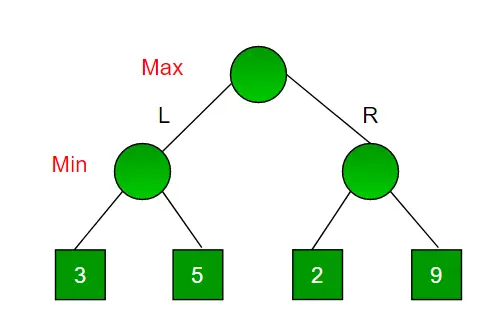
Poiché si tratta di un algoritmo basato sul backtracking, prova tutte le mosse possibili, quindi torna indietro e prende una decisione.
- Il massimizzatore va a SINISTRA: ora è il turno dei minimizzatori. Il minimizzatore ora può scegliere tra 3 e 5. Essendo il minimizzatore sceglierà sicuramente il minimo tra entrambi, ovvero 3
- Il massimizzatore va a DESTRA: ora è il turno dei minimizzatori. Il minimizzatore ora può scegliere tra 2 e 9. Sceglierà 2 poiché è il minimo tra i due valori.
Essendo il massimizzatore sceglieresti il valore più grande che è 3. Quindi la mossa ottimale per il massimizzatore è andare a SINISTRA e il valore ottimale è 3.
Ora l'albero del gioco appare come di seguito:

L'albero qui sopra mostra due possibili punteggi quando il massimizzatore effettua mosse a destra e a sinistra.
Nota: anche se nel sottoalbero di destra è presente un valore pari a 9, il minimizzatore non lo selezionerà mai. Dobbiamo sempre presumere che il nostro avversario giochi in modo ottimale.
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione dello stesso.
C++
ordinamento dell'heap
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Giava
casuale nessun generatore in Java
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
Javascript
dattiloscritto per ciascuno
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
Produzione:
The optimal value is: 12>
Complessità temporale: O(b^d) b è il fattore di ramificazione e d è il conteggio della profondità o dello strato del grafico o dell'albero.
Complessità spaziale: O(bd) dove b è il fattore di ramificazione in d è la profondità massima dell'albero simile a DFS.
L'idea di questo articolo è di presentare Minimax con un semplice esempio.
- Nell'esempio sopra, ci sono solo due scelte per un giocatore. In generale, ci possono essere più scelte. In tal caso, dobbiamo ricorrere a tutte le mosse possibili e trovare il massimo/minimo. Ad esempio, in Tic-Tac-Toe, il primo giocatore può effettuare 9 mosse possibili.
- Nell'esempio sopra ci vengono forniti i punteggi (foglie di Game Tree). Per un gioco tipico, dobbiamo ricavare questi valori
Presto tratteremo Tic Tac Toe con l'algoritmo Minimax.
Questo articolo è stato fornito da Akshay L. Aradhya.
