IL comeLista() metodo di java.util.Arrays La classe viene utilizzata per restituire un elenco di dimensioni fisse supportato dall'array specificato. Questo metodo agisce come a ponte tra API basate su array e basate su raccolte , in combinazione con Collection.toArray(). L'elenco restituito è serializzabile e implementa RandomAccess.
Mancia: Questo viene eseguito in tempo O(1).
Sintassi:
public static List asList(T... a)>
parametri: Questo metodo prende il matrice a che deve essere convertito in un Elenco. Qui... è conosciuto come vararg che è un array di parametri e funziona in modo simile a un parametro di array di oggetti.
Nota speciale: Il tipo di array deve essere una classe wrapper (Integer, Float, ecc.) in caso di tipi di dati primitivi (int, float, ecc.), ovvero non puoi passare int a[] ma puoi passare Integer a[]. Se passi int a[], questa funzione restituirà un List e non List , poiché in questo caso l'autoboxing non avviene e int a[] viene esso stesso identificato come oggetto e viene restituito un List of int array, invece di list di numeri interi, che genereranno errori in varie funzioni di raccolta.
Valore di ritorno: Questo metodo restituisce a visualizzazione elenco dell'array specificato.
Esempio 1:
Giava
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Produzione
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Esempio 2:
Giava
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
scanner javaProduzione
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Esempio 3:
Giava
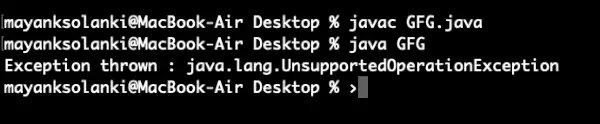
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Produzione: